We are excited to announce the official release of ESP-Audio-Effects v1.0.0! This is a powerful and flexible audio processing library designed to provide developers with efficient audio effects processing capabilities. You can now visit the ESP-Audio-Effects release page for more details. ESP-Audio-Effects is widely used in various smart audio devices, including smart speakers, headphones, audio playback devices, and voice interaction systems. Let’s dive into ESP-Audio-Effects now and enhance your audio processing capabilities!
Introduction to ESP-Audio-Effects Component#
ALC(Automatic Level Control): By adjusting the audio gain, the input audio volume is automatically regulated. When the gain is set to a positive value, the audio volume increases; when set to a negative value, the volume decreases. A gradual adjustment approach is used to prevent sudden volume changes, ensuring a smoother and more natural audio transition. If the gain is set too high, it will dynamically adjust the gain in real-time to keep the audio signal within a reasonable range, preventing distortion caused by clipping.
EQUALIZER: By precisely controlling the filter type, gain, frequency, and Q factor of each frequency band, precise audio tuning and optimization can be achieved. This approach offers greater flexibility than a graphic equalizer, making it suitable for professional audio engineering. It can effectively address specific frequency issues and enhance overall audio quality.
FADE: By setting the fade-in and fade-out times, smooth transitions between audio can be achieved. When playing new audio, the FADER automatically fades out the old audio while gradually fading in the new audio, preventing abrupt audio changes and enhancing the user experience.
SONIC: By adjusting the speed and pitch, SONIC enables audio speed and pitch manipulation. It processes the audio in real-time, allowing it to be played at different speeds and pitches, providing users with a richer and more diverse audio experience.
MIXER: By combining multiple input audio signals into a single output signal, the process adjusts the starting weight, target weight, and transition time for each audio signal. This ensures a harmonious and balanced audio output, where the final result blends the different signals seamlessly.
DATA WEAVER: It is primarily used for data interleaving and de-interleaving functions. (cfr. Data Layaout)
RATE CONVERSION: It is used for audio sample rate conversion, supporting conversions between various sample rates that are integer multiples of 4000 and 11025.
CHANNEL CONVERSION By setting a weight array, the audio signal can be converted from one channel layout to another.
BIT CONVERSION It is used for audio signal bit depth conversion, supporting mutual conversion between U8, S16, S24, and S32 bit depths.
Data Layout#
The component supports both interleaved and deinterleaved formats for input data.
Interleaved format: You can call the
esp_ae_xxx_process()interface. In multi-channel audio, such as stereo, the interleaved format arranges the samples sequentially, for example:L0 R0 L1 R1 L2 R2 ...Among them, L and R represent the data of the left and right channels, respectively.
Deinterleaved format: You can call the
esp_ae_xxx_deintlv_process()interface. In deinterleaved format, the data for each channel is stored separately, for example:L1, L2, L3, ... (Left Channel) R1, R2, R3, ... (Right Channel)The data of each channel is stored in various independent buffers.
API Style#
The component adopts a unified and simple API design, with a clear and intuitive interface style. Developers can easily perform audio processing through the following functions:
| Category | Function | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Initialization | esp_ae_xxx_open( ) | Create the audio effects handle for using. |
| Audio Process with interleave | esp_ae_xxx_process( ) | Processes audio data in the interleaved format. |
| Audio Process with deinterleave | esp_ae_xxx_deintlv_process( ) | Processes audio data in the deinterleaved format. |
| Set Parameter | esp_ae_xxx_set_xxx( ) | Sets specific parameters for the audio effect component. |
| Get Parameter | esp_ae_xxx_get_xxx( ) | Retrieves the current parameters of the audio effect component. |
| Release | esp_ae_xxx_close( ) | Closes the audio effect component and releases resources. |
Example of Using Audio Effects in GMF#
Each function of esp-audio-effects has been added to the esp-gmf (General Multimedia Framework) framework as a gmf-audio element. By integrating these audio effect elements through a pipeline, flexible combinations of audio processing can be achieved. You can see an example of pipeline in the picture below.
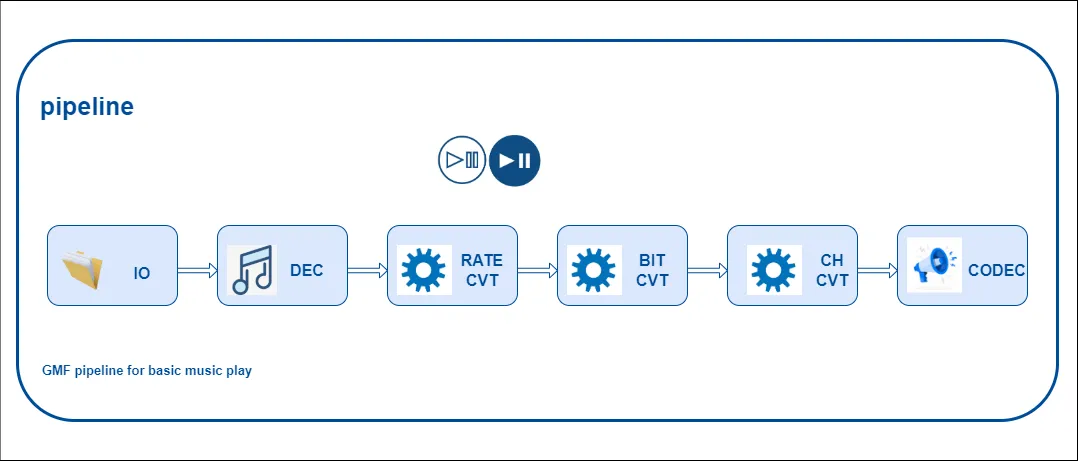
GMF Pipeline Sketch Map
Here is a simple example of how to use esp-audio-effects in GMF.
Conclusion#
ESP-Audio-Effects v1.0.0 is a versatile audio processing library. With features like Automatic Level Control, Equalizers, Dynamic Range Control, and more, it offers developers more control over audio effects. Through seamless integration with esp-gmf, developers can create easily create audio pipelines tailored to their application.
If you want to learn more about esp-audio-effects, check out our Github repository. Feel free to contact us and let’s explore more possibilities in audio processing together!





