Preface#
Amazon FreeRTOS is the latest offering (after acquisition of FreeRTOS) from Amazon that tries to simplify cloud connectivity with Amazon services (e.g. Shadow, Green-grass etc.) It has support for multiple micro-controller platforms from different vendors. Our ESP32 is now officially supported in Amazon FreeRTOS.
In this article we will discuss about —
- ESP32 integration in Amazon FreeRTOS (using existing ESP-IDF )
- Getting Started with ESP32 using Amazon FreeRTOS
Architecture#
Let us dig deeper in architecture of this offering in the context of ESP32 -
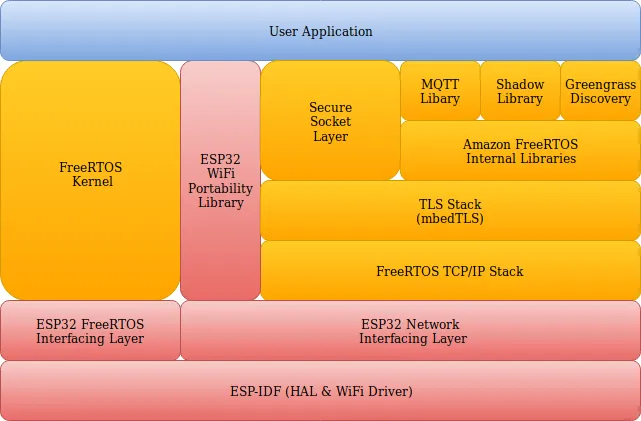
- Upstream or vanilla FreeRTOS had no support for theESP32 architecture (Xtensa LX6 dual core CPU). Support for this architecture is now available in the FreeRTOS V10 kernel . As of now it only supports single core mode of operation.
- A slightly modified version of the ESP-IDF is part of the Amazon FreeRTOS SDK itself. This IDF has all the required components including, hardware abstraction layer, Wi-Fi driver and other components that do not conflict with the ones already available in Amazon FreeRTOS SDK (e.g. Networking Stack, TLS stack etc.). Such a self contained package allows easier certification process as well.
- The WiFi portability layer acts as an abstraction, providing consistent application interface between different vendor platforms. Mostly the API for this layer helps in Wi-Fi interface/state management (Station and SoftAP) and power management.
- Another abstration layer is the secure socket layer shown above. It provides consistent application interface between different vendor’s network platforms (some of the vendors use custom Networking Stack) and interfacing with the mbedTLS stack.
Qualification#
The Amazon FreeRTOS Qualification Program (Amazon FQP) is for microcontroller (MCU) vendors for qualifying platforms (not SoC itself), and both ESP32-DevKitC and ESP-WROVER-KIT are certified in the latest release.
For more information please refer to, https://aws.amazon.com/freertos/partners/
Getting Started#
Please refer to the official Getting Started Guide on the AWS website for latest instructions on working with Amazon FreeRTOS: https://docs.aws.amazon.com/freertos/latest/userguide/getting_started_espressif.html
Examples#
Please refer to https://docs.aws.amazon.com/freertos/latest/userguide/freertos-mds-projects-struct.html for navigating to examples, primarily includes:
- MQTT — Client that both subscribes to and publishes to the same MQTT topic, as a result of which each time the MQTT client publishes a message to the remote MQTT broker, the broker sends the same message back to the client
- Shadow — Simple lightbulb example to illustrate how client application and things communicate with the Shadow service
- Greengrass — Simple example that performs discovery of AWS greengrass core device
Future Road-map (Near Term)#
Support for secure OTA updates using AWS is in Beta phase, please refer to, https://docs.aws.amazon.com/freertos/latest/userguide/freertos-ota-dev.html
This is certainly very important feature and as it evolves, all qualified vendors will support this, including Espressif.
This is still at early stage, please stay tuned as expecting some exciting road-map (with potential of use-cases it can cover) here!



