Assignment 4: Try using NVS#
As you can see from the last assignment, the Wi-Fi credentials were stored hard-coded. This is not the ideal solution for storing this kind of data, because mainly you can not change them easily, and, what is more important, this adds vulnerability to your project.
On this assignment, we will see how to store data to Non-Volatile-Storage (NVS). NVS is often called “emulated EEPROM”, but the ESP32 does not have any embedded EEPROM, so NVS uses flash memory.
The NVS library was designed to store small key-value pairs, including integer, string, and blob types.
String values are currently limited to 4000 bytes. This includes the null terminator. Blob values are limited to 508,000 bytes or 97.6% of the partition size - 4000 bytes, whichever is lower.
This library can be used to store several different configurations or values you will need to persist on the flash memory.
Hands-on with NVS#
For this hands-on, we will need to prepare a project for NVS, create the NVS data file with the Wi-Fi credentials, set the default values, add the NVS code, and change the example to read the Wi-Fi credentials from the NVS.
- Create the partition file
To create the partition table file, use the Partition Table Editor from the Espressif-IDE. To open the editor, right-click on the project, ESP-IDF -> Partition Table Editor:
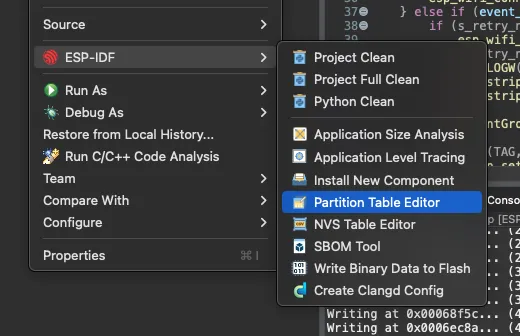
Leave the default values and click Save and Quit.
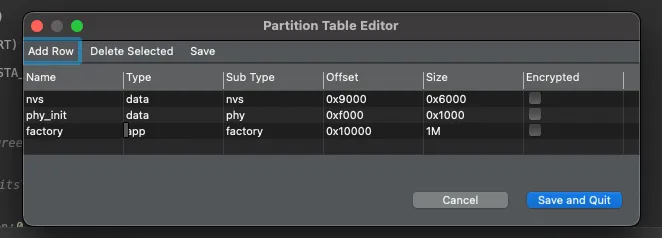
The default partitions.csv will be created with the following structure:
# ESP-IDF Partition Table
# Name, Type, SubType, Offset, Size, Flags
nvs, data, nvs, 0x9000, 0x6000,
phy_init, data, phy, 0xf000, 0x1000,
factory, app, factory, 0x10000, 1M,
You can change later the partitions according to your needs.
- Create the NVS data file
For the NVS editor, you will need to open the editor by going to ESP-IDF -> NVS Table Editor.
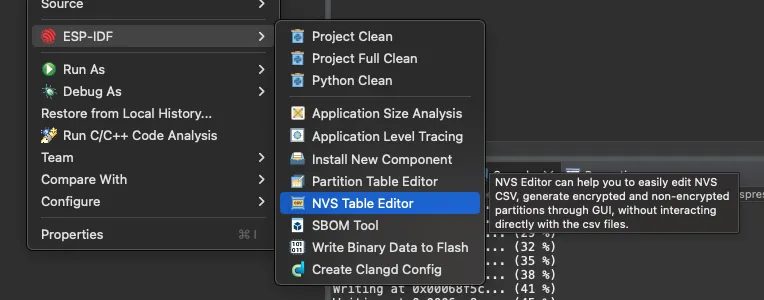
After that, add the namespace storage and the keys SSID and password, then click Save and Quit.
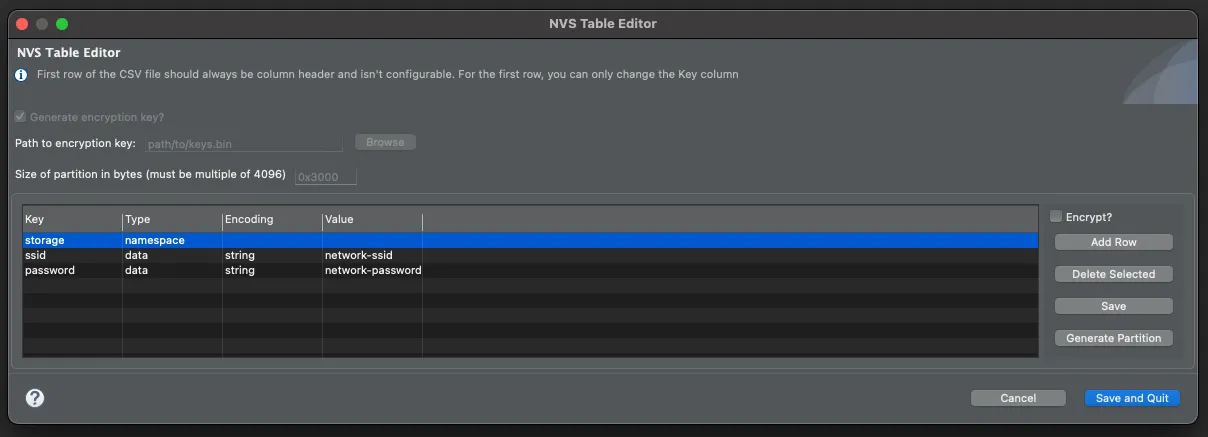
Set the Size of partition in bytes to 0x6000 (the same value as in the partitions.csv file) and add the following:
- storage type
namespace, - ssid type
data, encodingstringand valuenetwork-ssid - password type
data, encodingstringand valuenetwork-password
Please change the SSID and password values according to the workshop network or the network you will connect to.
After the NVS table is created, the file nvs.csv will be added to the project with the following content:
key,type,encoding,value
storage,namespace,,
ssid,data,string,"network-ssid"
password,data,string,"network-password"
- Include the NVS code
After the NVS initialization, the partition can be opened:
ESP_LOGI(TAG, "Opening Non-Volatile Storage (NVS) handle");
nvs_handle_t my_handle;
ret = nvs_open_from_partition("nvs", "storage", NVS_READWRITE, &my_handle);
if (ret != ESP_OK) {
ESP_LOGE(TAG, "Error (%s) opening NVS handle!\n", esp_err_to_name(ret));
return;
}
ESP_LOGI(TAG, "The NVS handle successfully opened");
Then the values from the NVS can be read:
char ssid[32];
char password[64];
esp_err_t get_wifi_credentials(void){
esp_err_t err;
ESP_LOGI(TAG, "Opening Non-Volatile Storage (NVS) handle");
nvs_handle_t nvs_mem_handle;
err = nvs_open_from_partition("nvs", "storage", NVS_READWRITE, &nvs_mem_handle);
if (err != ESP_OK) {
led_strip_set_pixel(led_strip, 0, 25, 0, 0);
led_strip_refresh(led_strip);
ESP_LOGE(TAG, "Error (%s) opening NVS handle!\n", esp_err_to_name(err));
return err;
}
ESP_LOGI(TAG, "The NVS handle successfully opened");
size_t ssid_len = sizeof(ssid);
size_t pass_len = sizeof(password);
err = nvs_get_str(nvs_mem_handle, "ssid", ssid, &ssid_len);
ESP_ERROR_CHECK(err);
err = nvs_get_str(nvs_mem_handle, "password", password, &pass_len);
ESP_ERROR_CHECK(err);
nvs_close(nvs_mem_handle);
return ESP_OK;
}
Now you need to change the Wi-Fi config to get the NVS values:
wifi_config_t wifi_config = {
.sta = {
.ssid = "",
.password = "",
.threshold.authmode = WIFI_AUTH_WPA2_WPA3_PSK,
.sae_pwe_h2e = WPA3_SAE_PWE_BOTH,
.sae_h2e_identifier = "",
},
};
strncpy((char*)wifi_config.sta.ssid, ssid, sizeof(wifi_config.sta.ssid));
strncpy((char*)wifi_config.sta.password, password, sizeof(wifi_config.sta.password));
Call the get_wifi_credentials before wifi_init_sta in the app_main function:
ESP_ERROR_CHECK(get_wifi_credentials());
- Change the build to include the NVS
Now you need to change the file main/CMakeLists.txt to add the nvs_create_partition_image.
idf_component_register(
SRCS main.c # list the source files of this component
INCLUDE_DIRS # optional, add here public include directories
PRIV_INCLUDE_DIRS # optional, add here private include directories
REQUIRES # optional, list the public requirements (component names)
PRIV_REQUIRES # optional, list the private requirements
)
nvs_create_partition_image(nvs ../nvs.csv FLASH_IN_PROJECT)
- Change the default configuration file to change the SDKConfig
If you do not have the file sdkconfig.defaults, create one in the same folder as the sdkconfig file and add the following configuration:
CONFIG_PARTITION_TABLE_CUSTOM=y
CONFIG_PARTITION_TABLE_CUSTOM_FILENAME="partitions.csv"
CONFIG_PARTITION_TABLE_FILENAME="partitions.csv"
This will trigger the binary creation with the predefined values from the nvs.csv file.
Now you can handle and change the SSID and password as you prefer directly from the NVS.
Assignment Code#
#include <stdio.h>
#include "bsp/esp-bsp.h"
#include "led_indicator_blink_default.h"
#include "freertos/FreeRTOS.h"
#include "freertos/task.h"
#include "freertos/event_groups.h"
#include "esp_system.h"
#include "esp_wifi.h"
#include "esp_event.h"
#include "esp_log.h"
#include "nvs.h"
#include "nvs_flash.h"
#include "lwip/err.h"
#include "lwip/sys.h"
#define WIFI_CONNECTED_BIT BIT0
#define WIFI_FAIL_BIT BIT1
char ssid[32];
char password[64];
static led_indicator_handle_t leds[BSP_LED_NUM];
static EventGroupHandle_t s_wifi_event_group;
static int s_retry_num = 0;
static const char *TAG = "workshop";
static void event_handler(void* arg, esp_event_base_t event_base,
int32_t event_id, void* event_data)
{
if (event_base == WIFI_EVENT && event_id == WIFI_EVENT_STA_START) {
esp_wifi_connect();
} else if (event_base == WIFI_EVENT && event_id == WIFI_EVENT_STA_DISCONNECTED) {
if (s_retry_num < 30) {
esp_wifi_connect();
s_retry_num++;
ESP_LOGW(TAG, "Trying to connect to WiFi");
led_indicator_set_rgb(leds[0], SET_IRGB(0, 0x0, 0x0, 0x20));
} else {
xEventGroupSetBits(s_wifi_event_group, WIFI_FAIL_BIT);
}
ESP_LOGE(TAG, "Failed to connect to WiFi");
led_indicator_set_rgb(leds[0], SET_IRGB(0, 0x20, 0x0, 0x0));
} else if (event_base == IP_EVENT && event_id == IP_EVENT_STA_GOT_IP) {
ip_event_got_ip_t* event = (ip_event_got_ip_t*) event_data;
ESP_LOGI(TAG, "got ip:" IPSTR, IP2STR(&event->ip_info.ip));
led_indicator_set_rgb(leds[0], SET_IRGB(0, 0x0, 0x20, 0x0));
s_retry_num = 0;
xEventGroupSetBits(s_wifi_event_group, WIFI_CONNECTED_BIT);
}
}
void wifi_init_sta(void)
{
s_wifi_event_group = xEventGroupCreate();
ESP_ERROR_CHECK(esp_netif_init());
ESP_ERROR_CHECK(esp_event_loop_create_default());
esp_netif_create_default_wifi_sta();
wifi_init_config_t cfg = WIFI_INIT_CONFIG_DEFAULT();
ESP_ERROR_CHECK(esp_wifi_init(&cfg));
esp_event_handler_instance_t instance_any_id;
esp_event_handler_instance_t instance_got_ip;
ESP_ERROR_CHECK(esp_event_handler_instance_register(WIFI_EVENT,
ESP_EVENT_ANY_ID,
&event_handler,
NULL,
&instance_any_id));
ESP_ERROR_CHECK(esp_event_handler_instance_register(IP_EVENT,
IP_EVENT_STA_GOT_IP,
&event_handler,
NULL,
&instance_got_ip));
wifi_config_t wifi_config = {
.sta = {
.ssid = "",
.password = "",
.threshold.authmode = WIFI_AUTH_WPA2_WPA3_PSK,
.sae_pwe_h2e = WPA3_SAE_PWE_BOTH,
.sae_h2e_identifier = "",
},
};
strncpy((char*)wifi_config.sta.ssid, ssid, sizeof(wifi_config.sta.ssid));
strncpy((char*)wifi_config.sta.password, password, sizeof(wifi_config.sta.password));
ESP_ERROR_CHECK(esp_wifi_set_mode(WIFI_MODE_STA) );
ESP_ERROR_CHECK(esp_wifi_set_config(WIFI_IF_STA, &wifi_config) );
ESP_ERROR_CHECK(esp_wifi_start() );
EventBits_t bits = xEventGroupWaitBits(s_wifi_event_group,
WIFI_CONNECTED_BIT | WIFI_FAIL_BIT,
pdFALSE,
pdFALSE,
portMAX_DELAY);
if (bits & WIFI_CONNECTED_BIT) {
ESP_LOGI(TAG, "Connected!");
} else if (bits & WIFI_FAIL_BIT) {
ESP_LOGE(TAG, "Failed to connect!");
}
}
esp_err_t get_wifi_credentials(void){
esp_err_t err;
ESP_LOGI(TAG, "Opening Non-Volatile Storage (NVS) handle");
nvs_handle_t nvs_mem_handle;
err = nvs_open_from_partition("nvs", "storage", NVS_READWRITE, &nvs_mem_handle);
if (err != ESP_OK) {
ESP_LOGE(TAG, "Error (%s) opening NVS handle!\n", esp_err_to_name(err));
return err;
}
ESP_LOGI(TAG, "The NVS handle successfully opened");
size_t ssid_len = sizeof(ssid);
size_t pass_len = sizeof(password);
err = nvs_get_str(nvs_mem_handle, "ssid", ssid, &ssid_len);
ESP_ERROR_CHECK(err);
err = nvs_get_str(nvs_mem_handle, "password", password, &pass_len);
ESP_ERROR_CHECK(err);
nvs_close(nvs_mem_handle);
return ESP_OK;
}
void app_main(void)
{
esp_err_t ret = nvs_flash_init();
if (ret == ESP_ERR_NVS_NO_FREE_PAGES || ret == ESP_ERR_NVS_NEW_VERSION_FOUND) {
ESP_ERROR_CHECK(nvs_flash_erase());
ret = nvs_flash_init();
}
ESP_ERROR_CHECK(ret);
ESP_ERROR_CHECK(bsp_led_indicator_create(leds, NULL, BSP_LED_NUM));
led_indicator_set_rgb(leds[0], SET_IRGB(0, 0x0, 0x0, 0x20));
ESP_ERROR_CHECK(get_wifi_credentials());
wifi_init_sta();
}
Next step#
Too complicated? Let’s make things easier.
